When it comes to architectural design and construction, the choice of materials can significantly influence both aesthetics and functionality. Among these materials, glass stands out as a versatile option that can enhance the beauty of a building while providing essential benefits such as natural light, energy efficiency, and weather resistance. However, with a myriad of glass types available, the question arises: Which glass is best for the exterior? This article delves into the various types of glass suitable for exterior applications, their properties, and the factors to consider when making a selection.
Understanding the Types of Glass for Exterior Use
- Tempered Glass
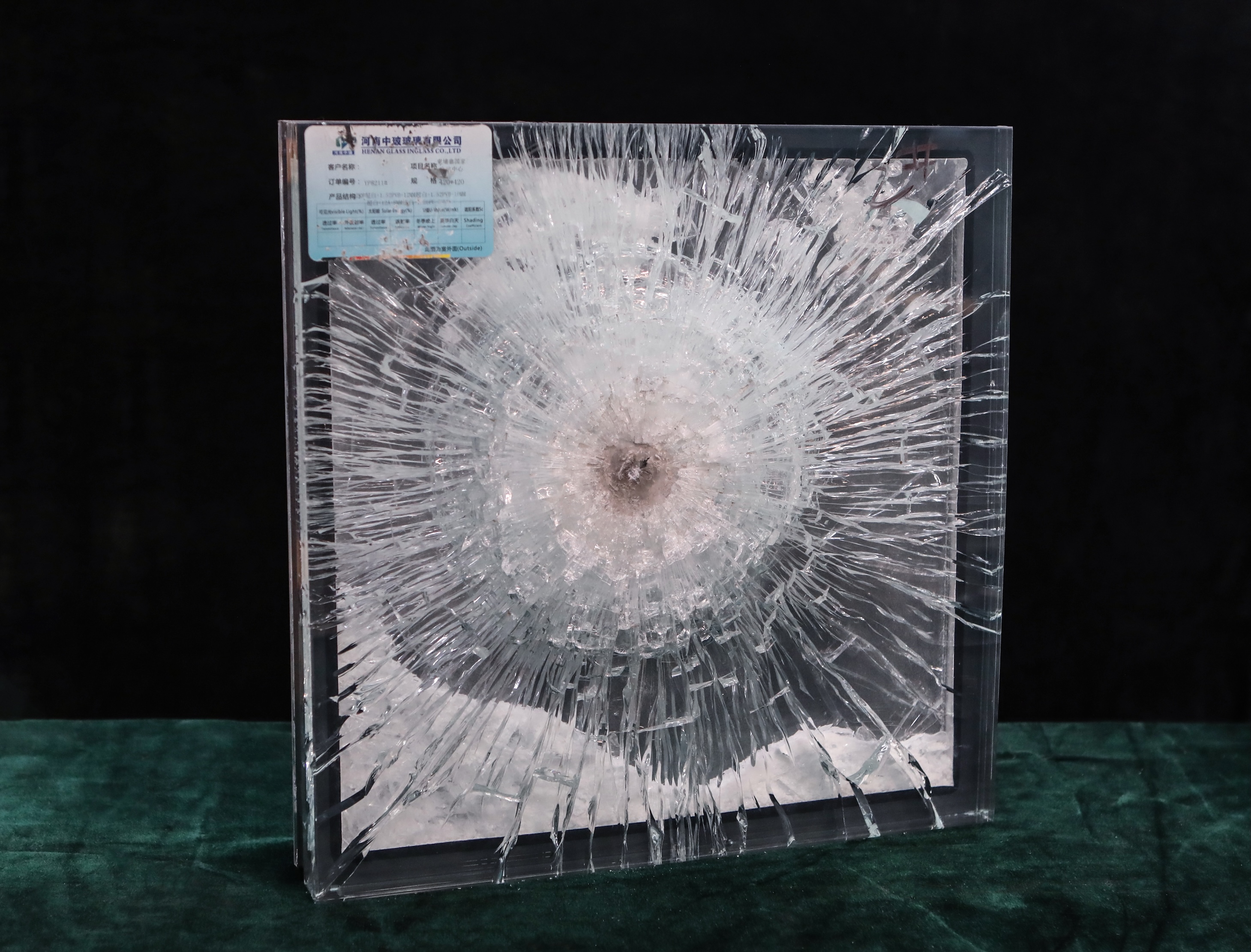
Tempered glass, also known as toughened glass, is produced through a process of extreme heating and rapid cooling. This treatment increases its strength, making it up to five times stronger than standard glass. It is an excellent choice for exterior applications due to its resistance to thermal stress and impact. In the event of breakage, tempered glass shatters into small, blunt pieces, reducing the risk of injury. Common uses include storefronts, curtain walls, and glass doors. - Laminated Glass
Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with an interlayer, typically made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB). This type of glass offers superior safety and sound insulation. In the event of breakage, the interlayer holds the glass fragments together, preventing them from falling and reducing the risk of injury. Laminated glass is ideal for areas prone to high winds or potential impacts, such as coastal buildings or high-rise structures. - Low-E Glass
Low-emissivity (Low-E) glass is coated with a thin layer of metallic oxide that reflects infrared light while allowing visible light to pass through. This property enhances energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer, making it an excellent choice for exterior windows and facades. Low-E glass can help maintain comfortable indoor temperatures and reduce energy costs, making it a popular option for both residential and commercial buildings. - Insulated Glass Units (IGUs)
Insulated glass units consist of two or more panes of glass separated by a spacer and sealed to create an airspace. This design significantly improves thermal insulation and soundproofing. IGUs are commonly used in exterior windows and curtain walls, providing energy efficiency and comfort. They can also be combined with Low-E coatings for enhanced performance. - Fritted Glass
Fritted glass is coated with a ceramic paint that is baked into the surface, creating a textured finish. This type of glass is often used for aesthetic purposes, as well as to reduce glare and heat gain. Fritted glass can be an excellent choice for exterior applications where both design and functionality are essential, such as in sunshades or decorative facades.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Exterior Glass
- Climate and Location
The local climate plays a crucial role in determining the best type of glass for exterior applications. In areas with extreme temperatures, Low-E or insulated glass may be more suitable to enhance energy efficiency. Conversely, in regions prone to storms or high winds, tempered or laminated glass can provide the necessary strength and safety. - Building Design and Aesthetics
The architectural style and design of the building should also influence the choice of glass. For modern designs, large expanses of clear tempered glass may be preferred for a sleek look, while traditional buildings might benefit from the warmth of laminated glass with decorative elements. - Safety and Security
Depending on the building's location and purpose, safety and security considerations are paramount. Laminated and tempered glass offer enhanced safety features, making them ideal for public buildings, schools, and residential properties in high-crime areas. - Energy Efficiency
With rising energy costs and increasing environmental awareness, energy-efficient glass options are becoming more popular. Low-E and insulated glass units can significantly reduce heating and cooling costs, making them a wise investment for both residential and commercial properties. - Regulatory Compliance
It is essential to consider local building codes and regulations when selecting exterior glass. Many jurisdictions have specific requirements regarding safety, energy efficiency, and environmental impact that must be adhered to.
Conclusion
Selecting the right glass for exterior applications is a multifaceted decision that requires careful consideration of various factors, including safety, energy efficiency, aesthetics, and local climate. By understanding the different types of glass available and their respective properties, architects, builders, and homeowners can make informed choices that enhance the functionality and beauty of their buildings. Whether opting for the strength of tempered glass, the safety of laminated glass, or the energy efficiency of Low-E glass, the right choice can lead to a more sustainable and visually appealing structure.